Introduction
The antifibrinolytic market represents a critical segment within the global hemostasis and thrombosis therapeutic landscape, encompassing medications designed to prevent or reduce excessive bleeding by inhibiting the fibrinolytic system. These pharmaceutical agents play a vital role in clinical medicine by blocking the natural process of clot dissolution, making them essential tools for managing bleeding disorders, surgical procedures, and trauma care. Antifibrinolytic drugs work by inhibiting plasmin activation or activity, thereby preventing the breakdown of fibrin clots that are essential for hemostasis.
Antifibrinolytic agents are classified into several categories based on their mechanism of action and chemical structure. The primary classes include lysine analogs such as tranexamic acid and aminocaproic acid, serine protease inhibitors like aprotinin, and synthetic inhibitors that target specific components of the fibrinolytic cascade. These medications are administered through various routes including intravenous, oral, and topical applications, depending on the clinical indication and severity of bleeding.
The global antifibrinolytic market serves diverse medical specialties including cardiac surgery, orthopedic surgery, trauma care, obstetrics and gynecology, and hematology. The market encompasses both prescription medications used in hospital settings and over-the-counter formulations for specific indications. The complexity of the market reflects the varied clinical applications and the need for specialized formulations tailored to specific patient populations and medical conditions.
Understanding the antifibrinolytic market requires examining its role in modern healthcare systems where surgical procedures are increasingly complex and patient populations present higher bleeding risks. The market’s growth is driven by advancing surgical techniques, increasing prevalence of bleeding disorders, and growing awareness of the clinical benefits of prophylactic antifibrinolytic therapy. The development of new formulations and delivery methods continues to expand therapeutic possibilities.
The market’s significance extends beyond direct therapeutic applications to encompass its role in improving patient outcomes, reducing healthcare costs, and enabling more complex surgical procedures. Antifibrinolytic agents have become integral components of patient blood management programs, which aim to optimize patient care while minimizing exposure to allogeneic blood products. This comprehensive approach to bleeding management reflects the evolving understanding of hemostasis and the importance of targeted therapeutic interventions.
The Evolution of Antifibrinolytic Therapies
The development of antifibrinolytic therapies traces back to the early 20th century when researchers first began to understand the fibrinolytic system and its role in hemostasis. The initial discoveries regarding plasmin and its role in clot dissolution laid the foundation for developing agents that could inhibit this process. Early research focused on identifying natural inhibitors of fibrinolysis and understanding the physiological mechanisms that control bleeding and clotting.
The 1950s and 1960s marked significant breakthroughs in antifibrinolytic therapy with the development of aminocaproic acid (EACA) and tranexamic acid. These lysine analogs were discovered to effectively inhibit plasminogen activation by competing with lysine binding sites on plasminogen and fibrin. The introduction of these synthetic compounds revolutionized the treatment of bleeding disorders and provided clinicians with reliable tools for managing excessive bleeding.
The 1970s and 1980s witnessed the development of aprotinin, a serine protease inhibitor derived from bovine lung tissue. Aprotinin represented a different approach to antifibrinolytic therapy, targeting multiple components of the coagulation cascade including plasmin, kallikrein, and trypsin. Its introduction expanded the therapeutic options available to clinicians and demonstrated the potential for more comprehensive hemostatic management.
The 1990s brought increased clinical research and evidence-based medicine approaches to antifibrinolytic therapy. Large-scale clinical trials established the efficacy and safety profiles of existing agents while identifying optimal dosing regimens and clinical applications. This period saw the development of standardized protocols for antifibrinolytic use in cardiac surgery, orthopedic procedures, and trauma care.
The early 2000s were marked by safety concerns regarding aprotinin following reports of increased adverse events in some patient populations. This led to temporary market withdrawal and increased scrutiny of antifibrinolytic safety profiles. The experience highlighted the importance of comprehensive safety evaluation and risk-benefit analysis in antifibrinolytic therapy.
Recent developments have focused on developing safer, more effective antifibrinolytic agents with improved pharmacokinetic properties. The introduction of new formulations, including extended-release preparations and combination therapies, has expanded therapeutic options. Research into novel mechanisms of action and targeted delivery systems continues to advance the field.
The integration of personalized medicine approaches and pharmacogenomics into antifibrinolytic therapy represents the latest evolution in the field. Understanding individual patient responses to antifibrinolytic therapy based on genetic variations and biomarkers promises to optimize treatment outcomes while minimizing adverse effects. This personalized approach reflects the broader trend toward precision medicine in healthcare.
Market Trends Shaping the Industry
The antifibrinolytic market is experiencing several transformative trends that are reshaping industry dynamics and creating new opportunities for growth. The increasing adoption of patient blood management programs represents one of the most significant trends driving market expansion. Healthcare systems worldwide are implementing comprehensive strategies to optimize patient care while reducing exposure to allogeneic blood products, creating substantial demand for effective antifibrinolytic therapies.
The growing emphasis on evidence-based medicine and clinical guidelines has strengthened the position of antifibrinolytic agents in standard care protocols. Professional medical societies and regulatory agencies have developed comprehensive guidelines for antifibrinolytic use, creating more standardized approaches to therapy and increasing clinician confidence in these medications. This trend has led to broader adoption and more consistent prescribing patterns.
Surgical complexity and patient acuity continue to increase, creating greater demand for effective hemostatic management. Advanced surgical procedures, including complex cardiac operations, major orthopedic reconstructions, and trauma surgeries, require sophisticated bleeding control strategies. The trend toward more complex procedures drives demand for reliable antifibrinolytic agents that can support these challenging clinical scenarios.
The development of new formulations and delivery methods represents another significant trend in the antifibrinolytic market. Manufacturers are developing topical formulations, extended-release preparations, and combination products that offer improved convenience and efficacy. These innovations address specific clinical needs and expand the therapeutic applications of antifibrinolytic agents.
Cost-effectiveness and health economic considerations have become increasingly important in healthcare decision-making. Antifibrinolytic agents demonstrate significant cost savings by reducing bleeding complications, blood product utilization, and hospital length of stay. This economic value proposition strengthens the position of antifibrinolytic therapies in healthcare systems facing budget constraints and value-based care initiatives.
The trend toward outpatient and minimally invasive procedures has created new opportunities for antifibrinolytic applications. As more procedures move to outpatient settings, the need for effective bleeding control that supports safe discharge becomes increasingly important. Oral antifibrinolytic formulations and topical applications are particularly well-suited for these evolving care models.
Digital health technologies and data analytics are beginning to influence antifibrinolytic therapy management. Electronic health records, clinical decision support systems, and predictive analytics tools help clinicians optimize antifibrinolytic use and monitor patient outcomes. This digitalization trend enhances the precision and effectiveness of antifibrinolytic therapy.
The growing focus on patient safety and adverse event prevention has driven improvements in antifibrinolytic formulations and monitoring practices. Enhanced safety profiles, better understanding of contraindications, and improved patient selection criteria have increased the therapeutic window for antifibrinolytic agents while reducing risks.
Challenges Facing the Market
The antifibrinolytic market faces numerous challenges that impact growth prospects and market development. Safety concerns and adverse event profiles represent one of the most significant challenges, particularly following the aprotinin controversy that highlighted potential risks associated with antifibrinolytic therapy. The need to balance efficacy with safety requires ongoing vigilance and comprehensive risk management strategies.
Regulatory complexity and varying approval processes across different regions create challenges for market access and product development. The stringent requirements for clinical trial data, safety monitoring, and post-market surveillance require substantial investments and expertise. Navigating diverse regulatory landscapes while maintaining compliance with evolving requirements presents ongoing challenges for manufacturers.
Competition from alternative hemostatic agents and blood conservation strategies poses challenges to traditional antifibrinolytic therapies. Factor concentrates, topical hemostatic agents, and mechanical bleeding control devices offer alternative approaches to bleeding management. The availability of multiple treatment options requires antifibrinolytic agents to demonstrate clear advantages and appropriate positioning in treatment algorithms.
Cost pressures and healthcare budget constraints limit market growth potential in some regions. Despite their cost-effectiveness, antifibrinolytic agents face scrutiny from payers and healthcare administrators seeking to control pharmaceutical expenditures. The need to demonstrate economic value while maintaining accessibility presents ongoing challenges for market expansion.
Clinical evidence gaps and the need for additional research in specific patient populations create challenges for market development. While substantial evidence supports antifibrinolytic use in many indications, some applications lack robust clinical data. The need for continued research and evidence generation requires ongoing investment and collaboration between manufacturers and clinical researchers.
Manufacturing and supply chain challenges affect product availability and market stability. The complexity of pharmaceutical manufacturing, quality control requirements, and supply chain management creates vulnerabilities that can impact product availability. Ensuring consistent supply while maintaining quality standards requires sophisticated manufacturing and distribution systems.
Physician education and awareness gaps limit optimal utilization of antifibrinolytic agents. Despite established clinical benefits, some healthcare providers remain unfamiliar with appropriate indications, dosing regimens, and monitoring requirements. The need for ongoing medical education and clinical support represents a significant challenge for market development.
Patent expiration and generic competition create pricing pressures for branded antifibrinolytic products. As patents expire, generic manufacturers enter the market with lower-priced alternatives, reducing profitability for innovative companies. The need to maintain competitive advantage while facing generic competition requires strategic planning and product differentiation.
Global market access and healthcare infrastructure limitations affect market penetration in developing regions. Limited healthcare resources, inadequate infrastructure, and regulatory barriers can restrict access to antifibrinolytic therapies in some markets. Addressing these challenges requires tailored approaches and potentially different product formulations or pricing strategies.
Market Scope and Applications
The scope of the antifibrinolytic market encompasses a diverse range of clinical applications across multiple medical specialties where bleeding control is critical. Cardiac surgery represents one of the largest market segments, with antifibrinolytic agents routinely used to reduce bleeding during complex procedures such as coronary artery bypass grafting, valve replacement, and aortic surgery. The high bleeding risk associated with cardiac surgery and the use of cardiopulmonary bypass systems create substantial demand for effective antifibrinolytic therapy.
Orthopedic surgery constitutes another significant market segment, particularly for major joint replacement procedures, spinal surgery, and trauma operations. The extensive tissue dissection and bone work involved in orthopedic procedures often result in significant bleeding, making antifibrinolytic agents valuable tools for improving surgical outcomes and reducing complications. The growing elderly population and increasing prevalence of degenerative joint diseases drive demand in this segment.
Trauma care and emergency medicine represent critical applications for antifibrinolytic therapy, particularly in managing traumatic bleeding and hemorrhagic shock. The time-sensitive nature of trauma care and the need for rapid bleeding control make antifibrinolytic agents essential components of trauma protocols. The increasing recognition of trauma-induced coagulopathy has expanded the role of antifibrinolytic therapy in emergency medicine.
Obstetrics and gynecology applications utilize antifibrinolytic agents for managing postpartum hemorrhage, menorrhagia, and bleeding associated with gynecological procedures. The unique physiological considerations in women’s health and the need for safe, effective bleeding control create specialized requirements for antifibrinolytic therapy. The growing awareness of maternal mortality related to bleeding complications drives demand in this segment.
Liver surgery and transplantation represent specialized applications where antifibrinolytic agents play crucial roles in managing the complex coagulopathy associated with liver disease. The impaired synthetic function of the liver and the extensive vascularity of hepatic procedures create challenging bleeding scenarios that benefit from antifibrinolytic support. The expansion of liver transplantation programs worldwide drives demand in this specialized segment.
Hematology and oncology applications encompass the use of antifibrinolytic agents in managing bleeding complications associated with blood disorders, chemotherapy, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Patients with hematological malignancies often experience bleeding complications due to thrombocytopenia, coagulopathy, or treatment-related effects. The growing incidence of hematological cancers and improved survival rates create ongoing demand for supportive care including antifibrinolytic therapy.
Dental and oral surgery applications represent growing market segments where antifibrinolytic agents are used to control bleeding during and after dental procedures. The oral cavity’s rich vascular supply and the challenges of achieving hemostasis in the oral environment make antifibrinolytic agents valuable tools for dental practitioners. The increasing complexity of dental procedures and the growing elderly population drive demand in this segment.
Pediatric applications require specialized considerations for antifibrinolytic therapy, including age-appropriate dosing, formulations, and safety profiles. Congenital bleeding disorders, pediatric cardiac surgery, and trauma care in children create unique requirements for antifibrinolytic agents. The growing recognition of pediatric bleeding disorders and improvements in pediatric surgical techniques drive demand in this specialized segment.
Market Size and Economic Impact
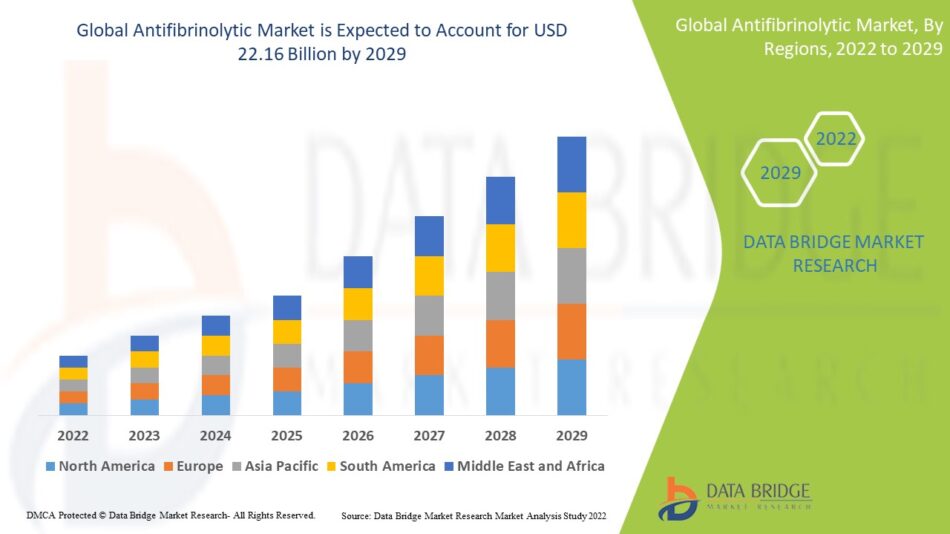
The global antifibrinolytic market represents a significant segment within the broader hemostasis and thrombosis therapeutic market, with substantial economic impact across healthcare systems worldwide. Market size estimates reflect the critical importance of these medications in modern medical practice and their widespread adoption across multiple clinical specialties. The market’s value encompasses both the direct costs of medications and the broader economic benefits derived from improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare utilization.
North America dominates the global antifibrinolytic market, accounting for the largest share of both consumption and revenue. The region’s advanced healthcare infrastructure, high surgical volumes, and comprehensive insurance coverage create favorable conditions for market growth. The United States, in particular, represents the largest single market for antifibrinolytic agents, driven by extensive use in cardiac surgery, orthopedic procedures, and trauma care.
Europe represents the second-largest regional market, with strong adoption of antifibrinolytic therapy across diverse healthcare systems. The region’s emphasis on evidence-based medicine and comprehensive healthcare coverage supports market growth. Countries such as Germany, the United Kingdom, and France represent key markets with established clinical practices and regulatory frameworks supporting antifibrinolytic use.
The Asia-Pacific region represents the fastest-growing market for antifibrinolytic agents, driven by expanding healthcare infrastructure, increasing surgical volumes, and growing awareness of bleeding management strategies. Countries such as China, India, and Japan are experiencing significant growth in healthcare expenditures and surgical procedures, creating substantial market opportunities for antifibrinolytic therapies.
The market’s economic impact extends beyond direct medication costs to encompass significant cost savings through reduced bleeding complications, decreased blood product utilization, and shorter hospital stays. Economic analyses consistently demonstrate that antifibrinolytic therapy provides substantial cost savings by preventing bleeding-related complications that would otherwise require expensive interventions and extended hospitalization.
Investment in research and development represents a significant component of the market’s economic impact. Pharmaceutical companies continue to invest in developing new antifibrinolytic agents, improved formulations, and expanded clinical applications. These investments drive innovation and create high-value employment opportunities in pharmaceutical research and development.
The market’s contribution to healthcare quality and patient outcomes represents substantial economic value that extends beyond direct cost considerations. By reducing bleeding complications, antifibrinolytic agents enable more complex surgical procedures, improve patient recovery, and reduce the risk of serious adverse events. This contribution to healthcare quality represents significant economic value for healthcare systems and society.
Manufacturing and supply chain activities associated with antifibrinolytic production create economic value through employment, industrial activity, and international trade. The specialized nature of pharmaceutical manufacturing requires skilled personnel and sophisticated facilities, contributing to economic development in manufacturing regions.
Factors Driving Growth
Multiple interconnected factors are driving sustained growth in the antifibrinolytic market, creating a favorable environment for expansion and innovation. The increasing surgical volume globally represents a fundamental driver of market growth, as healthcare systems worldwide perform more procedures requiring effective bleeding control. The aging population and increasing prevalence of conditions requiring surgical intervention create sustained demand for antifibrinolytic therapy.
The growing adoption of patient blood management programs represents a significant driver of market expansion. Healthcare systems are implementing comprehensive strategies to optimize patient care while reducing exposure to allogeneic blood products, creating substantial demand for effective antifibrinolytic therapies. These programs recognize antifibrinolytic agents as essential components of comprehensive bleeding management strategies.
Evidence-based medicine and clinical guidelines increasingly support the use of antifibrinolytic agents in diverse clinical scenarios. Professional medical societies and regulatory agencies have developed comprehensive guidelines for antifibrinolytic use, creating standardized approaches to therapy and increasing clinician confidence in these medications. This evidence-based approach drives broader adoption and more consistent prescribing patterns.
The increasing complexity of surgical procedures and higher patient acuity create greater demand for effective hemostatic management. Advanced surgical techniques, including complex cardiac operations, major orthopedic reconstructions, and minimally invasive procedures, require sophisticated bleeding control strategies. The trend toward more complex procedures drives demand for reliable antifibrinolytic agents that can support these challenging clinical scenarios.
Cost-effectiveness and health economic benefits provide strong drivers for market growth. Antifibrinolytic agents demonstrate significant cost savings by reducing bleeding complications, blood product utilization, and hospital length of stay. This economic value proposition strengthens the position of antifibrinolytic therapies in healthcare systems facing budget constraints and value-based care initiatives.
The expansion of outpatient and ambulatory surgical procedures creates new opportunities for antifibrinolytic applications. As more procedures move to outpatient settings, the need for effective bleeding control that supports safe discharge becomes increasingly important. Oral antifibrinolytic formulations and improved safety profiles make these agents well-suited for outpatient applications.
Growing awareness of trauma-induced coagulopathy and the importance of early intervention in bleeding management drives demand for antifibrinolytic therapy in emergency medicine. The recognition that early antifibrinolytic treatment can improve outcomes in trauma patients has led to expanded use in emergency departments and trauma centers worldwide.
Technological advancement in drug delivery and formulation development enables improved antifibrinolytic products with enhanced efficacy and safety profiles. The development of new formulations, including topical applications and extended-release preparations, expands therapeutic options and addresses specific clinical needs.
The increasing prevalence of bleeding disorders and conditions requiring long-term anticoagulation creates ongoing demand for antifibrinolytic therapy. As populations age and the use of anticoagulant medications increases, the need for effective bleeding control becomes more critical, driving demand for antifibrinolytic agents.
Regulatory support and favorable reimbursement policies in many regions create favorable conditions for market growth. Government health agencies and insurance providers increasingly recognize the value of antifibrinolytic therapy in improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs, supporting market access and utilization.
Educational initiatives and clinical training programs improve physician awareness and understanding of antifibrinolytic therapy. As healthcare providers become more familiar with appropriate indications, dosing regimens, and monitoring requirements, utilization of antifibrinolytic agents increases, driving market growth.
The market’s growth trajectory reflects the convergence of these multiple factors, creating a dynamic environment for continued expansion and innovation. The interplay between clinical evidence, economic considerations, and technological advancement continues to shape market development and create new opportunities for growth and value creation in the antifibrinolytic market.
Other Trending Reports
 WhatsApp Us Now
WhatsApp Us Now