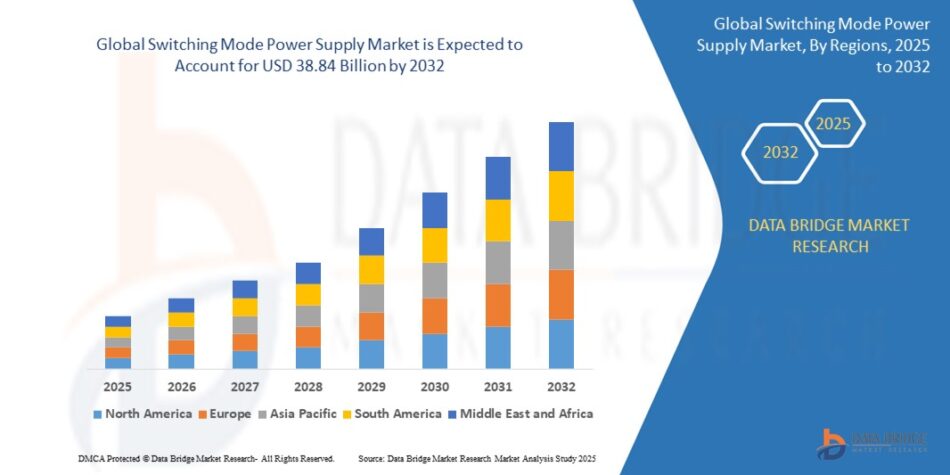
The Switching Mode Power Supply market was valued at USD 28.01 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 38.84 Billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 3.7% (2025-2032). Get insights on trends, segmentation, and key players with Data Bridge Market Research Reports.
Introduction
In the world of electronics, power supplies are the backbone that ensures devices receive the correct voltage and current to operate efficiently. Among the various types of power supplies, the Switching Mode Power Supply (SMPS) has become the preferred choice in modern electronic systems due to its high efficiency, compact size, and versatility. But what exactly is an SMPS, and how does it work? In this article, we’ll break down the fundamentals of Switching Mode Power Supplies, their components, operation principles, advantages, and common applications.
Definition
A Switching Mode Power Supply (SMPS) is an electronic power supply that converts electrical power efficiently by switching on and off rapidly using semiconductor devices, such as transistors, to regulate and stabilize output voltage. Unlike traditional linear power supplies, an SMPS minimizes energy loss by storing energy temporarily and releasing it in controlled pulses, making it lighter, more compact, and highly efficient for a wide range of applications, including computers, TVs, and industrial equipment.
What is a Switching Mode Power Supply?
A Switching Mode Power Supply is an electronic power converter that transforms electrical power efficiently by switching electronic components on and off at high frequencies. Unlike traditional linear power supplies that rely on dissipating excess voltage as heat, SMPS devices use high-frequency switching techniques and energy storage components like inductors and capacitors to regulate output voltage.
This switching action reduces power loss, making SMPS units smaller, lighter, and more energy-efficient compared to linear regulators. This is why SMPS technology is ubiquitous in everything from personal computers and smartphones to industrial equipment and renewable energy systems.
Basic Components of a Switching Mode Power Supply
To understand how an SMPS works, let’s look at its essential components:
Input Filter: This smooths out noise and prevents electromagnetic interference (EMI) from affecting the device or the electrical grid.
Rectifier and Filter: Transforms the incoming voltage from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). This DC voltage is then fed into the switching section.
Switching Element: Usually a transistor such as a MOSFET (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) or an IGBT (Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistor) that rapidly switches the current on and off.
Energy Storage Components: Inductors and capacitors store and release energy to smooth out voltage and current fluctuations caused by the switching action.
Control Circuit: Regulates the switching frequency and duty cycle to maintain a stable output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load.
Output Filter: Smooths the switched output to provide clean DC voltage to the load.
Feedback Circuit: Monitors the output voltage and sends signals to the control circuit to adjust switching parameters and maintain output stability.
How Does a Switching Mode Power Supply Work?
The core principle of an SMPS is rapidly switching the input voltage on and off and using energy storage components to regulate and smooth the output voltage. Here’s a step-by-step explanation:
AC to DC Conversion:
The SMPS usually starts by converting the incoming AC voltage from the mains (typically 110V or 220V) into an unregulated DC voltage using a rectifier and filter. The rectifier turns AC into pulsating DC, and the filter smooths this into a somewhat steady DC voltage.
High-Frequency Switching:
This unregulated DC voltage feeds into a high-speed switching transistor that turns on and off rapidly – often tens or hundreds of thousands of times per second (kHz to MHz range). This switching creates a pulsating DC waveform.
Energy Storage and Transformation:
The pulsating current flows through an inductor or a transformer (in isolated SMPS designs), which stores energy when the switch is on and releases it when the switch is off. The inductor or transformer smooths the pulsating current and, in transformer-based designs, also steps the voltage up or down to the desired level.
Output Filtering:
After the energy is transferred, the output passes through capacitors and sometimes additional inductors that filter out the high-frequency switching noise and ripple, producing a clean and stable DC output voltage.
Feedback Control:
A critical feature of SMPS is the feedback loop, which constantly monitors the output voltage. The control circuit modifies the duty cycle of the switch – the percentage of time the switch stays ON during each cycle – to compensate if the output voltage deviates from the intended value. Even when input voltage or load circumstances fluctuate, this keeps the output voltage constant.
Types of Switching Mode Power Supplies
SMPS units come in various configurations depending on the application and design requirements:
- Buck Converter (Step-Down): Transforms a higher input voltage into a lower output voltage.
- Boost Converter (Step-Up): Increases voltage from a lower input to a higher output voltage.
- Buck-Boost Converter: Can either step up or step down the voltage, providing versatility.
- Flyback Converter: Uses a transformer to provide isolation and voltage conversion; commonly used in low-power applications.
- Forward Converter: Similar to flyback but with continuous energy transfer, used for higher power.
- Half-Bridge and Full-Bridge Converters: Used for high-power applications with more complex switching.
Advantages of Switching Mode Power Supplies
Switching Mode Power Supplies offer several compelling advantages over traditional linear power supplies:
High Efficiency: Because the switching transistor operates in either fully ON or fully OFF states, power losses are minimized, often reaching efficiencies above 80-90%.
Compact Size and Light Weight: The use of high-frequency switching allows the use of smaller transformers and inductors, reducing size and weight.
Wide Input Voltage Range: SMPS can handle wide input voltage variations, making them suitable for global applications.
Less Heat Dissipation: High efficiency means less wasted energy as heat, reducing cooling requirements.
Flexible Output Voltages: They can provide multiple output voltages from the same supply using different converter topologies.
Common Applications of Switching Mode Power Supplies
SMPS units have become ubiquitous in electronic devices and systems due to their efficiency and versatility. Some common applications include:
- Computers and Laptops: Powering motherboards and peripherals with stable DC voltages.
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, TVs, gaming consoles, and audio equipment.
- Industrial Equipment: Control systems, automation, and robotics requiring reliable power.
- Telecommunications: Base stations, routers, and data centers.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Solar inverters and battery chargers.
- Electric Vehicles: Charging systems and onboard electronics.
Challenges and Considerations
While SMPS technology is powerful, it does come with some challenges:
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): High-frequency switching generates noise that can interfere with other devices if not properly managed.
- Complex Design: The control circuitry and components require careful design and testing.
- Cost: Components that are more intricate and occasionally more costly than linear power supply.
- Ripple and Noise: Despite filtering, some residual ripple and noise remain and can affect sensitive circuits.
Growth Rate of Switching Mode Power Supply Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the size of the global switching mode power supply market was estimated at USD 28.01 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.70% to reach USD 38.84 billion by 2032.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-switching-mode-power-supply-market
Conclusion
Switching Mode Power Supplies represent a fundamental advancement in power electronics, offering efficient, compact, and reliable power conversion solutions. By rapidly switching electrical current and harnessing energy storage components, SMPS units deliver stable DC output voltages from variable input sources with minimal energy loss.
 WhatsApp Us Now
WhatsApp Us Now