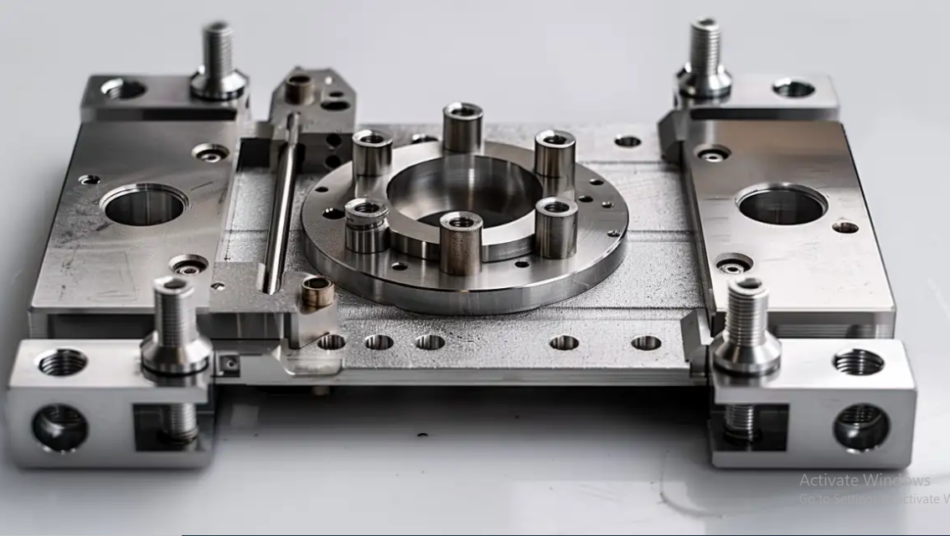
In modern manufacturing, precision and efficiency are key. One of the crucial components that help achieve these goals in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is the CNC fixture. A fixture is a tool or device used to securely hold a workpiece in place during the machining process, ensuring it is accurately positioned while being worked on by CNC machines. The right fixture can significantly enhance the performance of a CNC machine, making it an indispensable part of the manufacturing process. In this article, we will explore the purpose of CNC fixture, different types of fixtures, their applications, and why they are important in achieving precision in machining.
What is a CNC Fixture?
A CNC fixture is a specialized tool that holds and supports a workpiece during machining operations. Unlike a traditional clamp, which merely holds a workpiece in place, a CNC fixture is designed to hold the piece at specific angles, positions, or orientations, based on the requirements of the machining process. The fixture is essential for ensuring that the part being machined remains stationary, preventing any unwanted movement during the cutting, drilling, or milling operations.
Fixtures are used to position, support, and locate a part to ensure high repeatability and consistency, reducing the likelihood of errors or defects. They are commonly used in conjunction with CNC machines like CNC mills, CNC lathes, and CNC routers to produce parts with complex geometries.
Importance of CNC Fixtures in Manufacturing
CNC fixtures play a pivotal role in ensuring the accuracy and consistency of parts produced by CNC machines. Some of the key reasons why CNC fixtures are so important include:
1. Precision and Accuracy
The primary function of a CNC fixture is to secure the workpiece accurately. A well-designed fixture ensures that each part is positioned correctly, minimizing deviations in the cutting process. This results in high-precision machining, which is especially important when producing parts with tight tolerances and complex features. The fixture helps reduce errors that might occur due to manual handling or part shifting during the machining process.
2. Repeatability
Fixtures ensure that the workpiece is positioned identically for each machining operation. This repeatability is essential for mass production, where high volumes of parts need to be produced with consistent quality. CNC fixtures help to maintain uniformity across batches, ensuring that every part meets the same standards.
3. Increased Efficiency
By holding the workpiece securely and correctly, CNC fixtures allow the machining process to proceed without interruptions or adjustments. This reduces the need for manual re-positioning, leading to increased efficiency and faster production times. The use of CNC fixtures also helps prevent tool wear and damage, as parts are held firmly in place, reducing the chance of mistakes that might result in scrap material.
4. Reduced Labor Costs
Fixtures help automate the machining process by eliminating the need for manual adjustments or repositioning. This reduces the amount of time operators spend handling workpieces, leading to lower labor costs. Additionally, by improving efficiency and reducing errors, fixtures help manufacturers save on material costs by minimizing waste.
5. Enhanced Safety
A properly designed fixture ensures that the workpiece is held securely in place, reducing the risk of accidents caused by the part slipping or moving unexpectedly. This is particularly important in high-speed machining operations where any sudden movement can lead to damage to both the part and the machine, or even cause injury to operators.
Types of CNC Fixtures
CNC fixtures come in various forms, each tailored to meet specific machining requirements. The choice of fixture depends on factors such as the type of workpiece, the machining operation, and the required precision. Here are some of the most common types of CNC fixtures:
1. Vise Fixtures
Vise fixtures are among the most common and simple types of CNC fixtures. They are designed to hold a workpiece firmly between two jaws, which can be tightened using a screw or hydraulic system. Vises are ideal for holding parts with simple geometries, such as blocks or plates. They are often used in CNC milling machines for general-purpose machining operations.
2. Collet Fixtures
Collet fixtures use a collet to hold the workpiece in place. A collet is a type of clamp that tightly grips the workpiece by applying even pressure around its circumference. Collets are ideal for holding cylindrical parts such as shafts, rods, or tubes. This type of fixture is commonly used in CNC lathes and rotary machines, as it provides excellent concentricity and rigidity.
3. Magnetic Fixtures
Magnetic fixtures use powerful magnets to hold ferromagnetic workpieces in place. These fixtures are quick and easy to use, as they eliminate the need for mechanical clamping. Magnetic fixtures are ideal for flat, thin, or delicate parts that can be easily held using magnetic force. However, they are generally limited to ferrous materials like steel and iron and may not work for non-ferrous metals like aluminum or copper.
4. Vacuum Fixtures
Vacuum fixtures use suction to hold the workpiece in place. A vacuum is generated by a pump, creating negative pressure that pulls the part onto a flat surface. These fixtures are particularly useful for holding lightweight, flat, or delicate parts that cannot be clamped tightly without distortion. Vacuum fixtures are commonly used in CNC routers and 3D printing applications where the workpieces are thin or have intricate shapes.
5. Custom Fixtures
For complex or highly specific parts, manufacturers may opt for custom-designed CNC fixtures. These fixtures are tailored to the unique geometry of the workpiece and the machining operations it will undergo. Custom fixtures can include specialized features like adjustable clamps, locating pins, or support blocks to hold the workpiece securely. While custom fixtures can be more expensive and time-consuming to design and fabricate, they are often necessary for precision machining or when dealing with complex parts.
6. Turntable Fixtures
Turntable fixtures, often used in multi-axis CNC machines, allow the workpiece to be rotated at different angles for machining on multiple sides. These fixtures are useful for machining parts that require operations from several directions without the need to manually reposition the part. Turntable fixtures are commonly used in the automotive, aerospace, and mold-making industries for machining complex parts.
Applications of CNC Fixtures
CNC fixtures are used in various industries, where precision, repeatability, and efficiency are critical. Some common applications of CNC fixtures include:
1. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry relies heavily on CNC fixtures for producing parts like engine components, brackets, shafts, and housings. These parts often require high precision, and CNC fixtures ensure that the workpieces are held securely during machining, allowing for consistent quality and faster production.
2. Aerospace Industry
Aerospace components must meet strict safety and quality standards. CNC fixtures are used to machine complex and high-precision parts like turbine blades, wing components, and landing gear. Fixtures ensure that these parts are held firmly and accurately, reducing the risk of defects that could affect performance or safety.
3. Medical Device Manufacturing
In the medical device industry, CNC fixtures are used to manufacture components such as surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic devices. These parts often require high precision to ensure proper fit and function. CNC fixtures help ensure that each part is machined to exact specifications, improving patient safety and device performance.
4. Consumer Electronics
CNC fixtures are used in the manufacturing of consumer electronics like smartphones, laptops, and televisions. Precision fixtures are used to machine parts like housings, connectors, and internal components. Fixtures ensure the accuracy of these delicate parts, which often have tight tolerances and complex designs.
5. Tooling and Mold Making
CNC fixtures are essential in the creation of molds, dies, and tooling for various manufacturing processes. These fixtures help secure the mold components during machining, ensuring that they are precisely shaped and ready for use in mass production.
Conclusion
CNC fixtures are an integral part of the manufacturing process, providing the necessary support, stability, and precision to ensure the accurate machining of parts. They enhance efficiency, repeatability, and safety while reducing errors and production costs. With a variety of fixture types available—from simple vises to complex custom fixtures—manufacturers can select the right fixture for each job, ensuring that parts are machined to the highest standards. Whether in automotive, aerospace, medical, or electronics industries, CNC fixtures are essential for achieving the quality and precision required in modern manufacturing.
 WhatsApp Us Now
WhatsApp Us Now