Discover the key differences between stalemate vs checkmate in chess. Learn strategies, tips, and patterns to improve your game and play chess like a pro.
Chess is one of the most strategic and intellectually stimulating games in the world. Every move matters, and understanding the nuances of game-ending scenarios is crucial for players at all levels. Two terms that often confuse new players are stalemate and checkmate. While they may seem similar at first glance, their outcomes and strategic implications are very different. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the differences, strategies, and tips for play chess enthusiasts who want to improve their game.
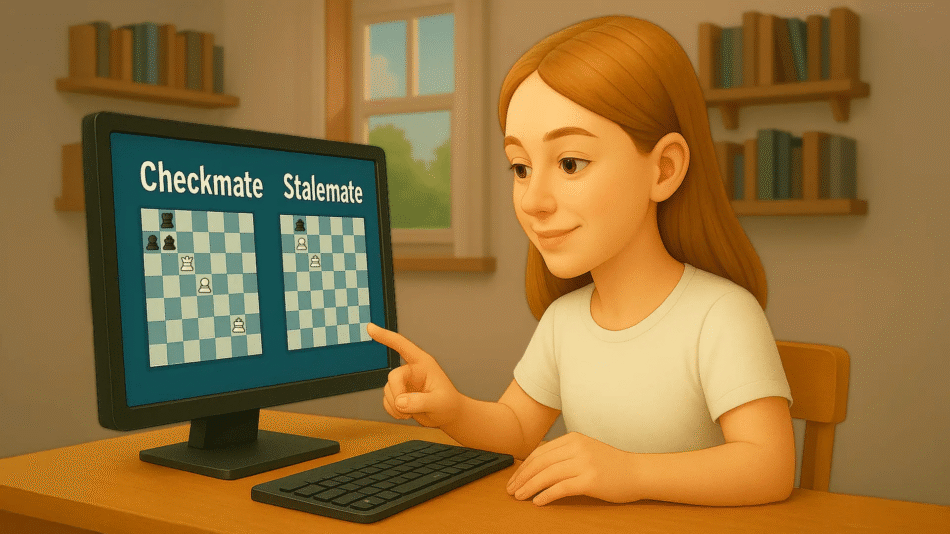
What is Checkmate?
Checkmate is the ultimate goal in chess. It occurs when a player’s king is under direct threat of capture and there is no legal move to escape the threat. In other words, checkmate ends the game immediately, awarding victory to the player delivering it. Recognizing checkmate patterns is essential for any player aiming to win consistently.
Key Features of Checkmate
- Game-ending move: Checkmate immediately concludes the game.
- King in danger: The king is under attack (in check) and cannot escape.
- Requires strategy: Achieving checkmate often involves careful planning and coordination between multiple pieces.
Some common checkmate patterns every player should know include:
- Back-rank mate: Often occurs when the opponent’s king is trapped behind its pawns.
- Smothered mate: Delivered when a king is surrounded by its own pieces and cannot move.
- Fool’s mate: A rare and fast checkmate that happens in just two moves.
Understanding these patterns can help you play chess more effectively and spot opportunities to win games faster.
What is Stalemate?
Stalemate, on the other hand, is a situation where a player has no legal moves left, but their king is not in check. Unlike checkmate, stalemate results in a draw, not a win. Stalemates often happen when a player miscalculates the endgame, accidentally allowing their opponent to gain a draw.
Key Features of Stalemate
- Draw outcome: The game ends in a draw, regardless of material advantage.
- King is safe: The king is not in check, which differentiates it from checkmate.
- Often accidental: Stalemates frequently occur due to poor planning or oversight.
For example, if you have a significant material advantage but leave the opponent with no legal moves without putting their king in check, you may unintentionally create a stalemate. Learning how to recognize and avoid stalemate scenarios is vital for improving your overall chess strategy.
Stalemate vs Checkmate: Understanding the Differences
While both stalemate and checkmate involve the king and can end a game, their differences are crucial. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Checkmate | Stalemate |
|---|---|---|
| Outcome | Win for the player delivering it | Draw |
| King Status | In check | Not in check |
| Game End | Immediate victory | Immediate draw |
| Strategy | Planned for finishing the game | Often accidental or defensive |
Recognizing the difference is essential to avoid turning a likely victory into a draw and to defend effectively against your opponent.
Why Understanding Checkmate Matters
Checkmate is the final goal of almost every chess game. Mastering checkmate strategies improves your ability to play chess efficiently and decisively.
Tips for Achieving Checkmate
- Control the board: Dominate key squares to limit your opponent’s movement.
- Coordinate pieces: Use multiple pieces in combination, like rooks, queens, and bishops, to trap the king.
- Plan ahead: Always think a few moves in advance to anticipate counterplays.
- Learn patterns: Study and memorize common checkmate patterns to execute them under pressure.
By incorporating these strategies, you can convert even slightly advantageous positions into victories.
Why Understanding Stalemate Matters
While checkmate focuses on winning, stalemate is about avoiding mistakes. Knowing how to spot potential stalemates can prevent frustrating draws when you have a winning position. It’s equally important to play chess defensively and force stalemates when facing a stronger opponent.
Tips to Avoid Stalemate
- Keep the king in check: If your goal is to win, ensure the opponent’s king is always under threat.
- Count available moves: Before moving a piece, check that the opponent still has legal moves.
- Know endgame patterns: Recognize positions where stalemate is likely, such as lone kings against a queen.
- Use pawns wisely: Avoid advancing pawns in a way that blocks the opponent’s king, unintentionally causing stalemate.
By understanding these tips, you can improve your endgame performance and maintain control until victory.
Common Scenarios Where Stalemate Occurs
- King trapped by own pieces: A player with only a king and a pawn may accidentally trap their own king.
- Overly aggressive opponent: Sometimes the winning player pushes too aggressively and corners the opponent’s king without giving them legal moves.
- Endgame mismanagement: When a player ignores potential stalemate positions, they may convert a winning position into a draw.
Recognizing these situations helps you both capitalize on and defend against stalemates.
Strategies to Force Checkmate
Winning a game requires a combination of strategic thinking and tactical execution. Here’s how to effectively force checkmate:
- Use forks and pins: These tactical maneuvers allow you to threaten multiple pieces, creating opportunities to trap the king.
- Limit king movement: Control escape squares to gradually corner the king.
- Exchange pieces wisely: Simplifying the board with exchanges can make delivering checkmate easier.
- Anticipate defenses: Predict the opponent’s potential moves and plan to counter them.
Practicing these strategies will enhance your ability to play chess with confidence and consistency.
Common Misconceptions About Stalemate and Checkmate
- Stalemate is a loss: Many beginners mistakenly believe stalemate is a loss, but it’s actually a draw.
- Checkmate is always obvious: Not every checkmate is straightforward. Some require multiple moves of planning.
- Stalemate only happens with few pieces: While more common in endgames, stalemates can occur in complex middle-game scenarios too.
Understanding these misconceptions can prevent confusion and help you develop a sharper chess strategy.
Conclusion
Understanding stalemate vs checkmate is fundamental for anyone who wants to improve at chess. While checkmate represents victory, stalemate emphasizes caution and awareness. By learning to identify both scenarios, you can refine your strategy, avoid costly mistakes, and become a stronger player.
FAQs About Stalemate and Checkmate
Q1: Can a game be a draw without a stalemate?
Yes, draws can occur due to insufficient material, threefold repetition, or the fifty-move rule.
Q2: Can checkmate happen accidentally?
While rare, inexperienced players can fall into an accidental checkmate if they fail to anticipate threats.
Q3: Should I aim for stalemate if I’m losing?
Absolutely. If you’re in a losing position, forcing a stalemate can save you from defeat.
Q4: How do I recognize potential stalemates?
Pay attention to the opponent’s available moves and ensure the king is not trapped without being in check.