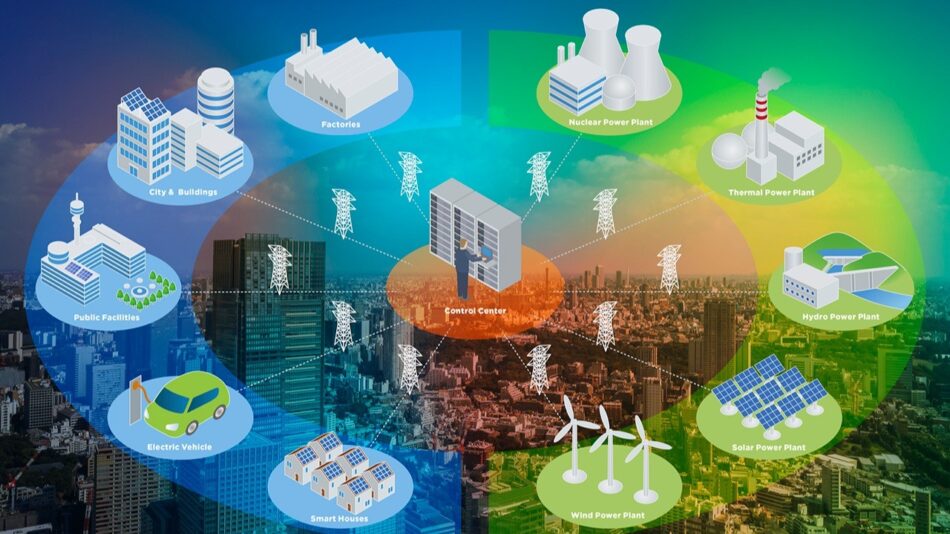
In today’s fast-changing power landscape, utilities face a dual challenge — balancing rising energy demand with sustainability goals. The old grid model, designed for one-way power flow, is no longer sufficient in an era defined by decentralization, digitalization, and decarbonization. This is where the Smart Grid System emerges as a transformative solution, enabling utilities to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and deliver uninterrupted energy to millions.
The idea isn’t just about modernizing infrastructure; it’s about making the entire power network more intelligent. From predictive analytics to automation and data-driven insights, a Smart Grid Power System empowers utilities to think smarter — not harder.
What Makes a Smart Grid System “Smart”?
A Smart Grid System integrates advanced digital communication, automation, and monitoring technologies into the traditional grid. It allows two-way communication between utilities and consumers, turning the power network into an intelligent ecosystem capable of self-assessment, fault detection, and real-time optimization.
At its core, the system connects key components such as SCADA systems, sensors, smart meters, and IoT-enabled devices. This integration gives utilities unprecedented visibility into every point of the network — from generation and transmission to distribution and consumption.
Unlike legacy grids that react to failures after they happen, smart grids anticipate and prevent them, improving efficiency and reliability.
How Smart Grid Systems Transform Utility Operations
Utilities today must deliver energy that’s not only reliable but also clean, affordable, and responsive. A Smart Grid Power System addresses these needs by digitizing control processes and automating decision-making.
Here’s how smart grids are helping utilities redefine their operational strategy:
1. Predictive Maintenance Over Reactive Repairs
Traditional grid systems rely on manual inspection and reactive maintenance, which often lead to costly downtimes. Smart grids, powered by sensors and SCADA system vendors, provide real-time data on equipment health. This data helps predict failures before they occur, reducing outages and maintenance costs.
2. Real-Time Load Management
With renewable energy integration and fluctuating demand, maintaining grid stability is complex. Smart grids allow utilities to balance load dynamically. Automated controls can reroute power or adjust supply instantly — ensuring efficient distribution and preventing overloads.
3. Faster Fault Detection and Restoration
When faults occur, smart grids can identify the exact location in seconds. Automated switching and remote isolation minimize downtime, allowing faster restoration. This level of responsiveness is vital in reducing SAIDI and SAIFI metrics — the benchmarks for power reliability.
4. Enhanced Renewable Integration
Solar, wind, and hybrid energy systems are becoming mainstream, but their intermittent nature challenges grid stability. Smart grid technologies integrate these renewable sources smoothly, balancing supply fluctuations and maintaining consistent voltage levels.
This not only supports sustainability goals but also enables utilities to manage diverse power inputs intelligently.
Smart Grids Benefits That Go Beyond Efficiency
While efficiency is the most obvious advantage, the benefits of smart grids extend far beyond technical gains. They redefine how utilities interact with energy and customers alike.
1. Improved Power Reliability and Quality
Smart grids significantly reduce outages, voltage fluctuations, and transmission losses. The result is a more reliable energy supply with fewer interruptions.
2. Better Energy Transparency
Consumers gain access to detailed data on their energy usage, helping them make informed decisions and reduce waste. This transparency fosters trust between utilities and customers.
3. Environmental Sustainability
By integrating renewable energy and improving transmission efficiency, smart grids play a crucial role in lowering carbon emissions. They help utilities align with global sustainability frameworks and national energy policies.
4. Cybersecurity and Data Integrity
Modern smart grid designs incorporate cybersecurity at their foundation. From encrypted communications to secure data protocols, utilities can protect operational data and prevent unauthorized access — a vital component in today’s interconnected energy world.

The Role of SCADA Systems in Smart Grid Evolution
One of the strongest backbones of any Smart Grid System is the SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) platform. SCADA systems enable utilities to collect, visualize, and control field data in real time.
Leading SCADA system vendors have evolved their platforms beyond monitoring — now integrating advanced analytics, AI, and edge computing to process data at lightning speed.
Through SCADA integration, utilities gain:
- Real-time situational awareness
- Centralized control of distributed assets
- Automated response to faults
- Enhanced coordination between substations
In essence, SCADA transforms the grid into a responsive, self-correcting system — making it the nerve center of every intelligent energy network.
Data Is the New Power Source
The biggest shift introduced by smart grids is the move from energy-based control to data-driven management. Every sensor, substation, and meter generates valuable insights.
This data allows utilities to forecast demand, monitor power quality, and manage distributed generation in real time.
With machine learning and AI now integrated into smart grid platforms, predictive modeling helps utilities anticipate peak loads, optimize renewable mix, and plan preventive maintenance — turning data into a competitive advantage.
Why Utilities Can’t Afford to Delay Smart Grid Adoption
Energy infrastructure is undergoing one of the most profound transformations in history. Delaying modernization exposes utilities to operational risks, revenue loss, and regulatory challenges.
Adopting a Smart Grid Power System is no longer about innovation; it’s about resilience. With the growing adoption of electric vehicles, renewable integration, and smart cities, future energy systems must be adaptive, intelligent, and self-sustaining.
Utilities that embrace smart grid technologies today position themselves as leaders of tomorrow’s power ecosystem.
Empower Progress with Hartek Group
As one of India’s top power and renewable infrastructure companies, Hartek Group has been instrumental in building smarter, more efficient energy systems.
From EPC and substation automation to Smart Grid System design and SCADA integration, Hartek delivers end-to-end solutions that redefine how utilities operate.
With a focus on innovation, reliability, and sustainability, Hartek is powering India’s transition toward a more intelligent energy future.

FAQs on Smart Grid System
1. What is a Smart Grid System?
A Smart Grid System is an advanced electrical network that uses automation, sensors, and digital communication to monitor and manage power flow efficiently. It enables real-time data exchange between utilities and consumers.
2. What are the main benefits of smart grids?
The key Smart Grids Benefits include improved reliability, better energy efficiency, seamless renewable integration, lower outages, and enhanced consumer engagement.
3. How does a Smart Grid Power System help utilities?
Smart grids empower utilities through real-time monitoring, load balancing, and fault detection. They allow predictive maintenance and efficient resource allocation, reducing both costs and downtime.
4. What role do SCADA system vendors play in Smart Grids?
SCADA system vendors provide the control platforms that collect, analyze, and visualize real-time power data. They enable automation, remote control, and advanced analytics essential for smart grid functionality.
5. Why should utilities upgrade now?
With increasing energy demand and renewable integration, upgrading to a smart grid ensures operational resilience, regulatory compliance, and long-term sustainability.
 WhatsApp Us Now
WhatsApp Us Now