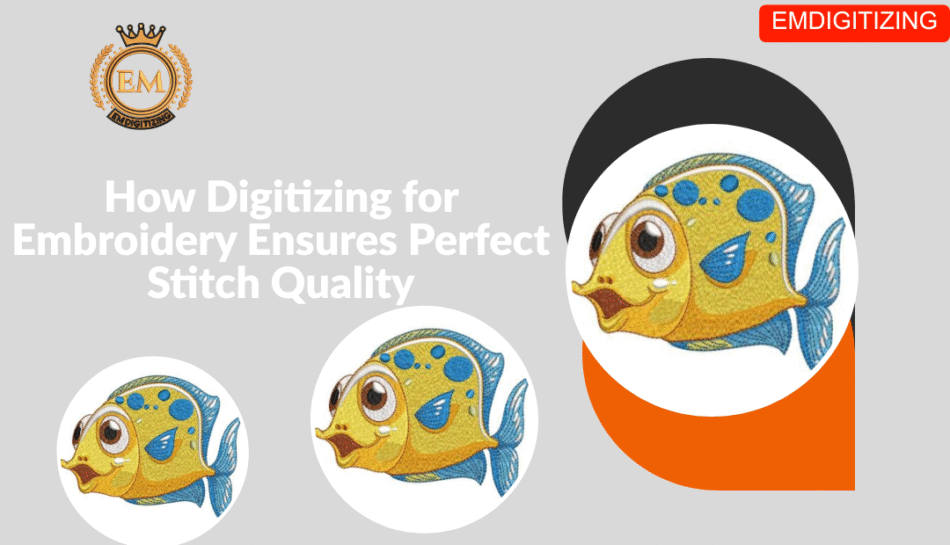
Digitizing for embroidery is the backbone of producing flawless, professional-looking embroidery. It’s not just about converting an image into stitchesit’s about ensuring each stitch is placed with precision for the perfect result. Whether you’re working with simple monograms or complex, multi-colored designs, the quality of digitizing can make or break your final output.
In this article, we’ll explore how digitizing for embroidery directly influences stitch quality, why it matters for your projects, and the techniques professionals use to achieve perfection.
Understanding Digitizing for Embroidery
Digitizing for embroidery is the process of converting artwork into a stitch file that an embroidery machine can read. This involves mapping out stitch types, directions, densities, and color sequences to ensure the design is sewn exactly as intended.
If the digitizing process is done incorrectly—such as using poor stitch density or improper underlay—the embroidery may appear distorted, uneven, or puckered. On the other hand, skilled digitizing ensures smooth lines, crisp edges, and a professional finish.
Why Stitch Quality Depends on Digitizing
Stitch quality is determined by the placement, density, and type of stitches used. Poorly digitized designs often lead to:
- Uneven stitches that make the design look sloppy.
- Thread breaks caused by excessive density.
- Fabric puckering from improper underlay settings.
- Distorted shapes due to wrong stitch direction.
Good digitizing prevents these problems, ensuring every stitch contributes to a beautiful final product.
Key Factors That Improve Stitch Quality
1. Stitch Type Selection
Choosing the right stitch type is essential for different elements of a design:
- Satin stitches for letters and borders.
- Fill stitches for large areas.
- Running stitches for outlines or fine details.
2. Optimal Stitch Density
Too much density can make the design stiff and cause thread breaks, while too little can make it look sparse. Professionals balance density based on fabric type and design requirements.
3. Proper Underlay
Underlay stitches act as a foundation for top stitches, preventing fabric shifting and improving overall stability.
4. Fabric-Specific Adjustments
Each fabric reacts differently to embroidery. For example:
- Light fabrics require lighter densities.
- Stretch fabrics need stabilizing underlay to avoid distortion.
5. Accurate Stitch Direction
Changing stitch angles adds texture and ensures the design catches light beautifully.
Role of Technology in Stitch Perfection
Modern embroidery software provides simulation tools, allowing digitizers to preview designs before stitching. This helps detect potential errors and make necessary adjustments, saving time and material.
Some advanced software even includes auto-adjust features that change density and stitch direction based on the fabric selected.
How Professionals Ensure High-Quality Stitches
Experienced digitizers follow these steps to ensure perfection:
- Analyze the artwork for complexity.
- Break the design into manageable sections for optimal stitching.
- Test sew-outs to detect and fix any issues.
- Adjust stitch settings for machine compatibility.
Conclusion
Perfect stitch quality in embroidery doesn’t happen by accident—it’s the result of careful planning and precise digitizing. By understanding fabric behavior, selecting the right stitch types, and using proper underlay, digitizing for embroidery can consistently produce stunning, professional results.
If you want flawless embroidery every time, invest in professional digitizing services. The right digitizer can transform your designs into machine-ready masterpieces with impeccable stitch quality.
FAQs
Q1: Can I digitize designs myself for good stitch quality?
Yes, but it requires learning digitizing software, understanding fabrics, and practicing test sew-outs.
Q2: What is the most common cause of poor stitch quality?
Incorrect density and lack of proper underlay are leading causes.
Q3: How does fabric type affect digitizing?
Different fabrics require unique settingsstretchy fabrics need stabilizers, while thick fabrics need looser densities.
Q4: Do professional digitizers use special software?
Yes, tools like Wilcom, Hatch, and Pulse offer advanced controls for stitch placement and density.
Q5: How can I test stitch quality before final production?
Always run a test sew-out on similar fabric to catch errors before bulk embroidery.